RESTful API
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
in Programming on NodeJS
if project size is getting bigger, we need to do modularization (MVC).
so, I created index.js file newly
index.js
// import file for basic
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
var router = express.Router();
var path = require('path')
// move the routers from app.js to index.js because all router will be stored in this file.
var main = require('./main')
var email = require('./email')
//url routing
router.get('/', function(req,res){
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, '../public/main.html')) });
router.use('/main',main)
router.use('/email',email)
module.exports = router;
app.js
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
var bodyParser = require('body-parser')
var router = require('./router/index')
app.listen(3000, function() {
console.log("start!! express server on port 3000"); });
// removed all lines related to router function
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended:true}))
app.set('view engine', 'ejs')
// only use index.js as a main router here.
// all detail router will be mentioned in index.js
app.use(router)
in Programming on NodeJS
html (request data to server with word) ->
server (receive data from server and return data) ->
html (receiver a data and print)
app.js
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
var bodyParser = require('body-parser')
app.listen(3000, function() {
console.log("start!! express server on port 3000");
});
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended:true}))
app.set('view engine', 'ejs')
// if html file call the /ajax_search
app.post ('/ajax_search', function(req, res){
console.log("Search Word is : "+req.body.searchword)
// data to send
var responseData = {'Searchword': req.body.searchword,
'Result1':'Result1','Result2':'Result2',
'Result3':'Result3','Result4':'Result4'}
//send data with json type
res.json(responseData)
});
form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="uft-8">
<title>Search engine</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post">
<input type="text" name="searchword"><br/>
</form>
<button class="ajaxsend">Search</button>
<div class="result"></div>
<script>
// if user click the button
document.querySelector('.ajaxsend').addEventListener('click',function(){
// take data from the form
var inputdata = document.forms[0].elements[0].value;
// call the function (sendAjax)
sendAjax('http://127.0.0.1:3000/ajax_search',inputdata);
})
function sendAjax(url, data){
// packing the data with string type
var data = {'searchword' : data};
data = JSON.stringify(data);
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('POST', url);
// declare the data is json type
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', "application/json");
// send a data
xhr.send(data);
// listen a event from the server.
xhr.addEventListener('load', function(){
// pasing from JSON type to string
var result = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
// Print a data with Ajax
for(var item in result){
document.querySelector(".result").innerHTML += item+" : "+result[item] +"<br>";
}
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
in Programming on NodeJS
like this picture, you can routing page with url easily.
app.js
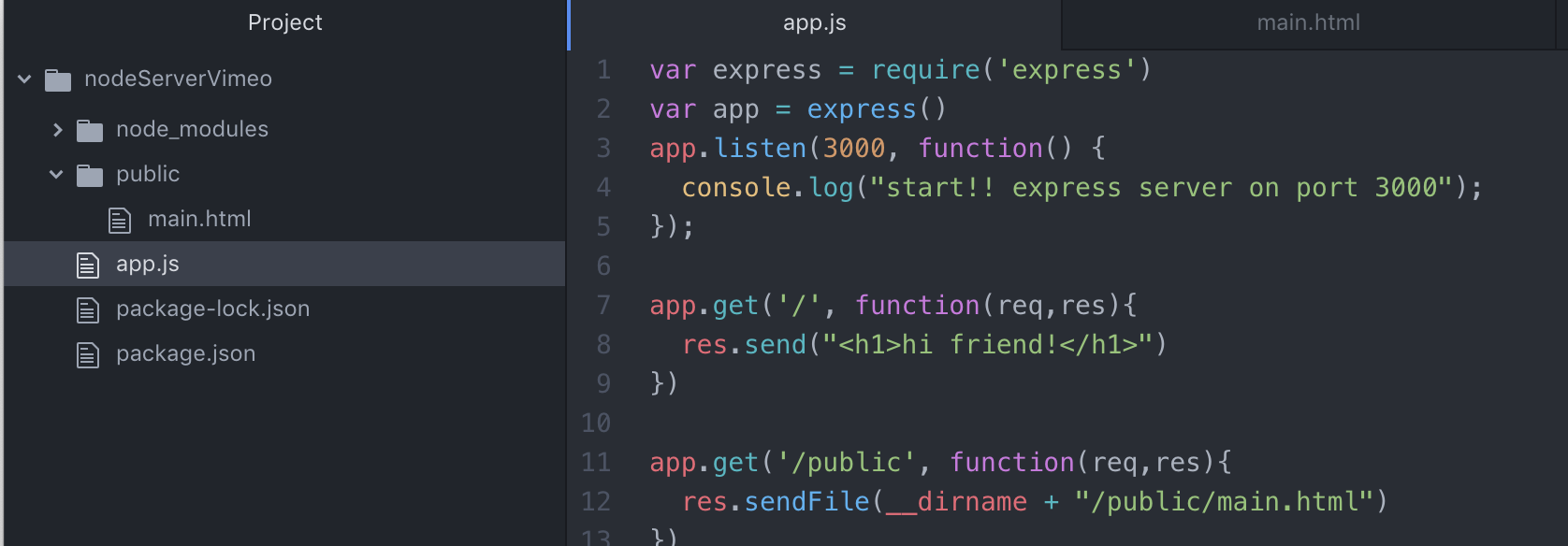 main.html
main.html
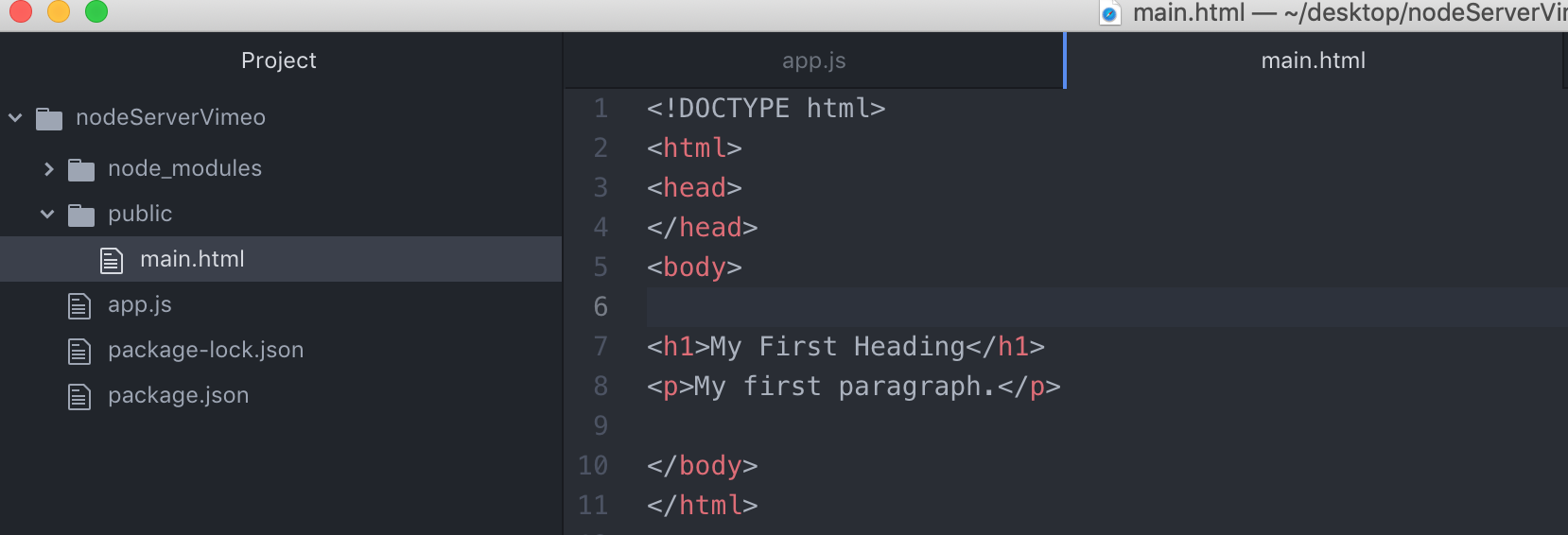 Internet browser
Internet browser
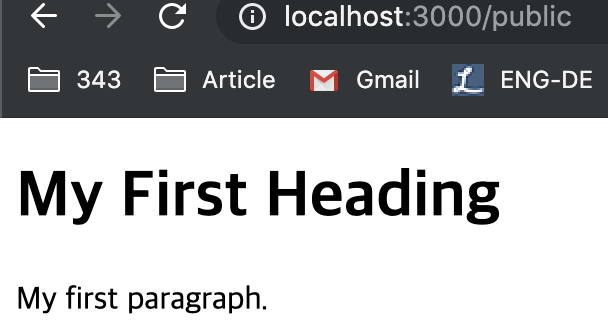
Also, if you use “app.use” function, server set public folder as a static.
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
app.listen(3000, function() {
console.log("start!! express server on port 3000");
});
//function app.use
app.use(express.static('public'))
//url routing
app.get('/', function(req,res){
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/public/main.html')
});
app.get('/main', function(req,res){
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/public/main.html')
});
in Programming on NodeJS
First of all, to parse data, we need to install body-parser
npm install body-parser --save
form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="uft-8">
<title>email form</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
<link rel="author" href="humans.txt">
</head>
<body>
<form action="/email_post" method="post">
email : <input type="text" name="email"><br/>
submit <input type="submit">
</form>
<script src="js/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
app.js
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
// declare bodyParser like as above code.
var bodyParser = require('body-parser')
app.listen(3000, function() {
console.log("start!! express server on port 3000");
});
app.use(express.static('public'))
// code could be json style
app.use(bodyParser.json())
// code could be encoded
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended:true}))
//url routing
app.get('/', function(req,res){
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/public/main.html')
});
app.get('/main', function(req,res){
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/public/main.html')
});
// if any page call the /email_post
// server will print req.body.email in console
// in case of form.html, the information should be content in input text for e-mail form
app.post ('/email_post', function(req,res){
//get : req.parm('email')
console.log(req.body.email)
res.send("post response");
});
in Programming on NodeJS
before init the npm, go to NodeJS website and download & install NodeJS
npm init
nodeserver installation. discription : nodeserver test and enter, enter, enter.
nodeserver
web framework download
npm install express --save
as you see express is now added on the dependencies.
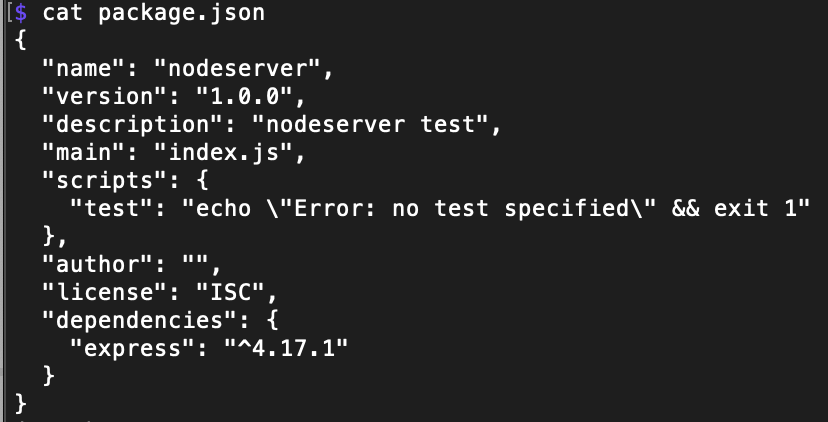
test server app.js
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
app.listen(3000, function()) {
console.log("start! express server on port 3000");
}
Synchronous first, Asynchronous last.
install nodemon
nodemon check a source code change and a pply the change automatically.
sudo install nodemon -g